Share the love
The average career of a MMA fighter is about 12 years provided he or she remains free from injury . On the other hand, 25% of professional careers unfortunately end before time due to neglect or improper management of Injuries.
If you are a a combat sport player or the parent of a child under martial arts training this blog may be vital for your knowledge understanding of these Injuries. And develop a scientific approach in dealing with injuries of the ankle and foot.
Foot and ankle injuries are common injuries in combat sports such as Karate , Taekwondo , jiu jitsu , Mixed martial arts etc . And are encountered during practise and competitions. Most of these Injuries are simple ones such as ankle and foot sprains commonly known as soft tissue trauma . They heal with first aid and rest.
Sometimes striking or twisting forces are strong enough to cause fractures and joint dislocations of foot and ankle bones, these Injuries need early detection and expert management.
Unrecognised soft tissue or bone Injuries lead to chronic pain or restricted foot or ankle mobility. And can seriously compromise performance of a player. Hence, injury awareness for the player and his coach , early recognition and expert management are vital for safe return to practise and performance.
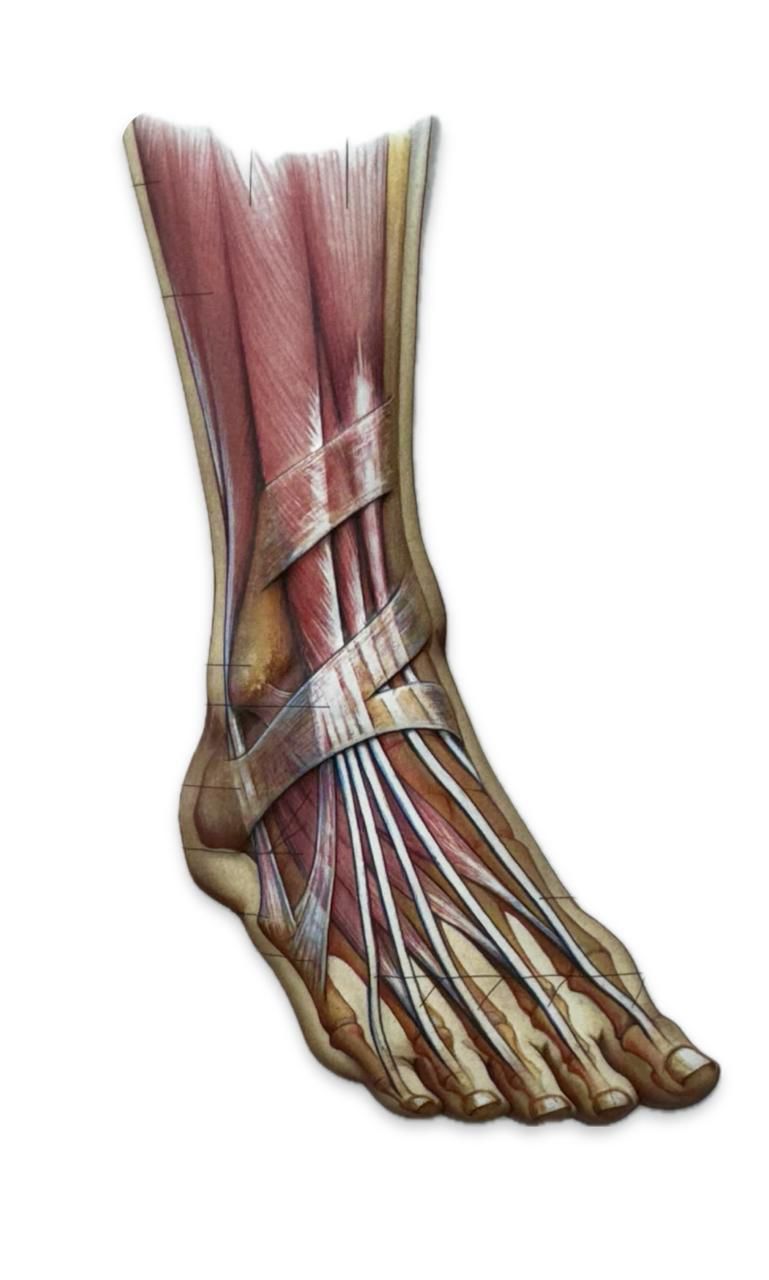
Contact and Non Contact Injury
As per Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine : Dec 2023
A player of combat sports can sustain injuries to foot and ankle joint during training and competition. Injuries occurring after a strike or accidental contact are called Contact Injury and non contact injuries can be self inflicted such as accidents in training.
Check the clip below :
Delving deeper in the topic , you may be surprised by the Statistics .
Published data reveals that 63% injuries are non contact and only 37% are contact injuries. Which thereby means, that more players are injured in training and sparring compared to the actual bouts in competitions.
This highlights the importance of proper technique and guidance in Combat Sports.
Another study published in Journal of Bone and Joint surgery – October 2023 ( Elsevier ) shows that female players are more prone to foot and ankle injuries compared to male players. Ankle injuries were more common in females than males (10.4 % versus 6.0 %)
Understanding the mechanism of injury
Check the clip below :
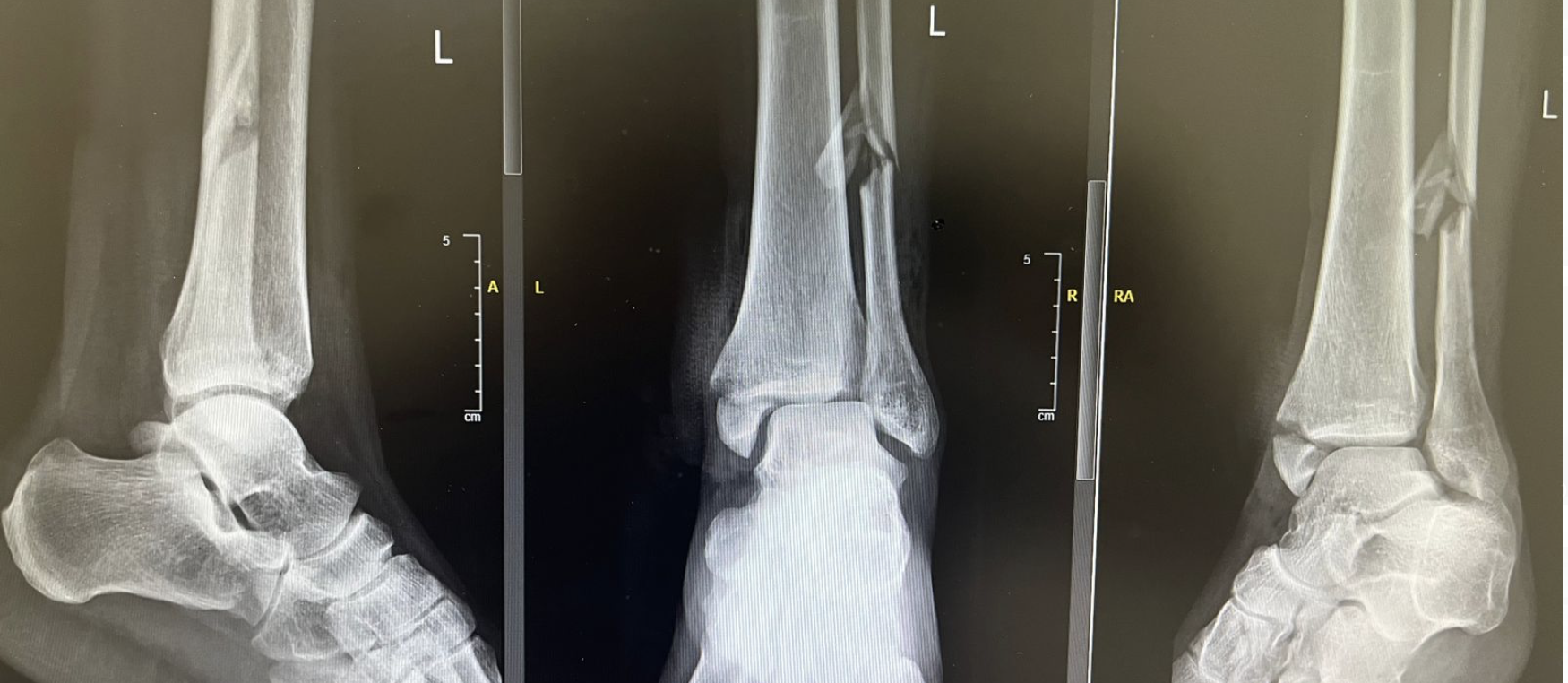
Multiple fractures around the ankle joint
Below is a common example of the type of Injuries sustained in the above situation.
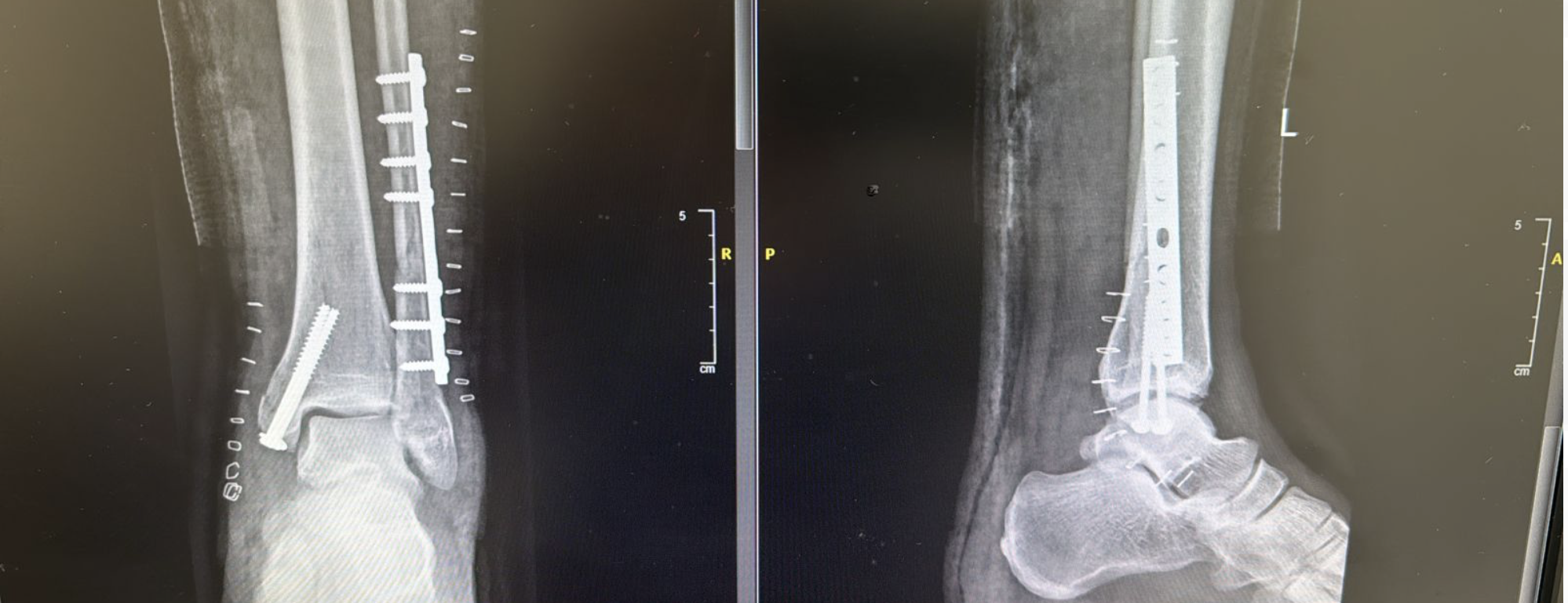
Fixation of fractures around the ankle joint
Below is a common example of the type of surgery done for the above Injuries. However, the fixation may vary from patient to patient as per fracture pattern.
How to identify and manage lower leg ankle & foot injuries?
These injuries cause severe pain, immediate swelling and deformity of the injured part.
When associated with a fracture there can be abnormal mobility and inability to bear weight on the part.
Sometimes, there can be blue discoloration of the injured part , change of skin color occurs due to bleeding in the skin , called ecchymosis. A response to direct impact.
But following a fracture or severe soft tissue injury, if the leg or foot becomes cold and blue, then it is a sign of a blood vessel injury or Compartment syndrome ( where blood in a tight muscle compartment strangulates blood circulation ). This is a surgical emergency! And needs immediate management by an orthopedic or trauma specialist.
Immediate Care
1. Reduction – Gently straighten the limb to resemble the normal one. Apply a sterile dressing pad if the skin is broken. Do not attempt to put weight on the limb.
2. Immobilization – using a splint or brace to prevents further damage. This can be ready made, pre fabricated ( synthetic or wood ), Fabricated – with cardboard, wooden struts and bandages or Plaster of Paris (POP ). POP splints are the most preferred.
3. Initial Treatment – Pain Management: take a dose of analgesics and anti-inflammatory medications to manage pain and swelling.
Start RICE Protocol:
Rest – Lie down or sit and don’t put weight on the injured part.
Ice – apply Ice packs,
Compression – compress the injured part with Crepe bandage
Elevation to reduce swelling , keep the leg at heart level.
4. Medical Attention – Transport the athlete to a medical facility for further evaluation and imaging, such as X-rays or CT scan to confirm the fracture type and severity under the guidance of an Orthopaedic and Trauma surgeon.
Non surgical management
Soft tissue injuries
Ankle sprains are the most common injuries in this category. And majority of them can be treated without surgery, however, the surgeon may sometimes advise a splint or plaster depending on the degree of injury. Few patients may need CT scan or MRI of the injured part to identify ligament Injuries. And for all players of combat sports it is very important to follow the instructions of your doctor.
As, ligament Injuries are the most commonly missed and become chronic. They can become worse with continued training or competition. Until finally, a treatable condition may force a precious talent to retire before time from the sport.
Surgical Management
Fractures, particularly those, where the broken fragments are displaced out of position or involving multiple fragments or breaking into joint surfaces, may require surgical fixation with plates, screws, metal pins or sometimes a metal frame.
After surgery the patient is not allowed to bear weight on the limb for 2-3 months on average and then may need physiotherapy to return to full activity.
If the implant is sticking out of the skin a minor stage II surgery may be needed after fracture union to remove the metal.
If the shape of the implant permits, after the fracture has united the player may restart running, CrossFit or kicking practice. But be advised to take your doctors permission after informing him what kind of activity you need to resume.
Removal of Metal implants
Many of you would like to know when can the implants be removed. Well, the general answer to this question is that at least 18 months after surgery. But, this period may widely vary according to:
– Type of fracture sustained by the player
– And type of metal implant fixed in the bone
– And also bone quality of the individual.
In short, the verdict on implant removal can be given only by the operating surgeon. And it is vital to respect this advice, because re fracture after implant removal is well known and this is a complicated problem.
Rehabilitation
1) Early Rehabilitation
Non-Weight Bearing Exercises:
The programme generally begins with gentle, non-weight-bearing muscle training exercises to maintain joint mobility and prevent stiffness.
Gradual Weight Bearing:
As healing progresses, gradually introduce weight-bearing activities under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
2) Strengthening and Conditioning
Muscle Strengthening:
Focuses on strengthening the muscles around the ankle, calf, and lower leg to restore stability and support. And quadriceps training drills for knee stability.
Balance and Proprioception:
followed by exercises to improve balance and proprioception ( joint feedback ), this is critical for preventing re-injury in martial arts training.
3) Functional Training:
sport-Specific Drills:
Reintroduce combat sport-specific movements, starting with low-intensity drills and gradually increasing the complexity and intensity.
Agility and Flexibility:
Work on agility and flexibility exercises to restore full functional capabilities.
Return to Training and Competition
1) Phased Return:
Gradual Progression:
Follow a phased return-to-play protocol, ensuring the athlete can perform techniques without pain or instability.
Monitoring: Regularly monitor the athlete’s progress and adjust the rehabilitation plan as needed.
2) Protective Measures:
Supportive Gear:
Use ankle supports or braces during training and competition to provide additional stability.
Proper Footwear:
Ensure the athlete wears appropriate, supportive footwear to minimize the risk of re-injury.
Preventive Strategies
1) Strength and Conditioning:
Regular Training:
Maintain a consistent regimen of strength and conditioning exercises focused on the lower extremities.
Flexibility:
Emphasize flexibility exercises to maintain a full range of motion in the ankle joint.
2) Technique and Training:
Proper Technique:
Ensure that athletes practice proper techniques to minimize undue stress on the ankles and feet.
Awareness and Education:
Educate athletes and coaches about the risks of ankle fractures and the importance of preventive measures.
In conclusion
Managing ankle & foot Injuries in combat sports involves prompt and accurate diagnosis, appropriate medical intervention, and a structured rehabilitation program.
Preventive strategies, including strength training, proper technique, and the use of supportive gear, are essential to minimize the risk of future injuries.
By following these guidelines, martial art practitioners can achieve a safe and efficient return to their sport, maintaining both their performance and long-term joint health.
For guidance and queries,
Reach out to our Orthopaedic and Trauma expert : Dr. Adarsh Kumar




